🚀 Welcome to Day 12 of the 90-Day DevOps Challenge! Today, we're diving deep into the heart of Git with a focus on essential git commands: merge, rebase, reset and revert. These commands form the backbone of efficient version control, enabling seamless collaboration and ensuring project success.
1. Git Rebase:
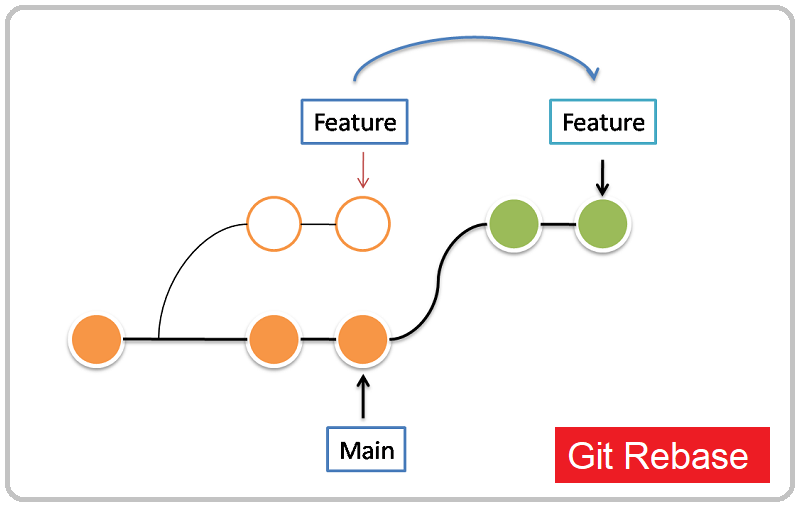
Git rebase is used to integrate changes from one branch onto another by reapplying commits on top of another base branch. This creates a linear history and helps keep your commit history clean.
# Start with a feature branch
git checkout feature_branch
# Rebase onto the main branch
git rebase main
Git rebase:Provides a linear commit history without merge commits.
2. Git Merge:

Git merge combines changes from different branches into one branch. It creates a merge commit that integrates changes from the source branch into the target branch.
# Switch to the target branch where you wants to merge changes
git checkout main
# Merge feature_branch into main
git merge feature_branch
Git merge: Creates a merge commit that integrates changes from the source branch.
3. Git Revert:
Git revert is used to undo a previous commit by creating a new commit that reverses the changes introduced by the specified commit.
# Revert the last commit
git revert HEAD
# Revert a specific commit
## commit_hash --> Unique number for every commit
git revert <commit_hash>
Git revert: Reverts changes introduced by the specified commit.
4. Git Reset:
Git reset is used to reset the current branch to a specific commit, either keeping the changes in the working directory or discarding them.
# Reset to a specific commit, keeping changes in the working directory
git reset <commit_hash>
# Reset to a specific commit, discarding changes in the working directory
git reset --hard <commit_hash>
Git reset: Resets the branch to a specific commit, keeping or discarding changes.
5. Git Stash:
Git stash temporarily shelves changes in the working directory, allowing you to switch branches or perform other tasks without committing changes.
# Stash changes
git stash
# Retrieve stashed changes
git stash pop
6. Git Ignore:
Git ignore specifies intentionally untracked files that Git should ignore. It's typically used to exclude files like build artifacts, logs, and dependencies from version control.
# Create or edit .gitignore file
nano .gitignore
# Add file patterns to ignore
*.log
/build/
Mastering Git commands like rebase, merge, revert, reset, git ignore, git stash, and git stash pop unlocks a world of possibilities in version control. With these tools at your disposal, you can navigate through complex scenarios with confidence, streamline collaboration, and ensure the success of your projects. 🚀💻 Embrace the power of Git commands, and let them guide you on your DevOps journey to new heights of efficiency and productivity! HappyLearning! #Devops90DaysChallenge 🌟👩💻
